Jenkins in Docker Ecosystem: Supercharging CI/CD with Full Docker Support
Jenkins is an open-source automation server widely used for building, testing, and deploying software. Developed in Java and launched in 2011, Jenkins has become a key tool in the DevOps toolchain, enabling continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) practices.
Getting Started
This documentation aims to guide you through the process of deploying Jenkins with Docker support and Blue Ocean plugin out-of-box using Docker Compose, providing a quick and easy setup for local development and testing.
Jenkins Server
We’ll need to build a custom Dockerfile to customize a Jenkins image and make some modifications, including installing Docker CLI, adding Blue Ocean Jenkins plugin.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
FROM jenkins/jenkins:latest USER root RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y lsb-release RUN curl -fsSLo /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.asc https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg RUN echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y docker-ce-cli USER jenkins RUN jenkins-plugin-cli --plugins "blueocean docker-workflow" ENV DOCKER_HOST=tcp://docker:2376 ENV DOCKER_CERT_PATH=/certs/client ENV DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY=1 EXPOSE 8080/tcp EXPOSE 5000/tcp
Jenkins Docker In Docker
This Dockerfile will enable us to run Docker commands from within a Docker container. The exposed port
2376is commonly used for secure communication with the Docker daemon. TheDOCKER_TLS_CERTDIRenvironment variable is used to specify the directory where TLS certificates are stored.1 2 3
FROM docker:dind EXPOSE 2376/tcp ENV DOCKER_TLS_CERTDIR=/certs
Docker Compose
Now, we need to define two services:
jenkins-serverandjenkins-docker-in-dockerin our Docker Compose file.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55
--- version: '3.8' services: # Jenkins Server jenkins-server: container_name: jenkins_server build: context: . dockerfile: ./jenkins/jenkins_server image: jenkins:built restart: unless-stopped volumes: - jenkins-data:/var/jenkins_home - jenkins-docker-certs:/certs/client:ro depends_on: - jenkins-docker-in-docker networks: - services # Jenkins Docker In Docker jenkins-docker-in-docker: container_name: jenkins_dind build: context: . dockerfile: ./jenkins/jenkins_dind image: jenkins_dind:built restart: unless-stopped privileged: true volumes: - jenkins-docker-certs:/certs/client - jenkins-data:/var/jenkins_home networks: services: aliases: - docker # Docker Networks networks: services: driver: bridge # Docker Volumes volumes: jenkins-data: driver: local driver_opts: type: 'none' o: 'bind' device: '$VOLUME_PATH/jenkins/data' jenkins-docker-certs: driver: local driver_opts: type: 'none' o: 'bind' device: '$VOLUME_PATH/jenkins/certs'
NOTE:
The aliases for the
dockernetwork in thejenkins-docker-in-dockerservice allow the Jenkins server to refer to the Docker daemon using the hostnamedocker.Ensure that the
$VOLUME_PATHvariable is correctly set in your environment or replace it with the actual path where you want to store Jenkins data and Docker TLS certificates.
Run the following command to start the containers:
1
docker-compose up -dAccess Jenkins Web Interface
Once the containers are running, access Jenkins in your web browser at
http://localhost:8080.Unlock Jenkins
Retrieve the initial admin password:
1
docker exec -it jenkins_server bash -c "cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword"
Creating First Jenkins Pipeline
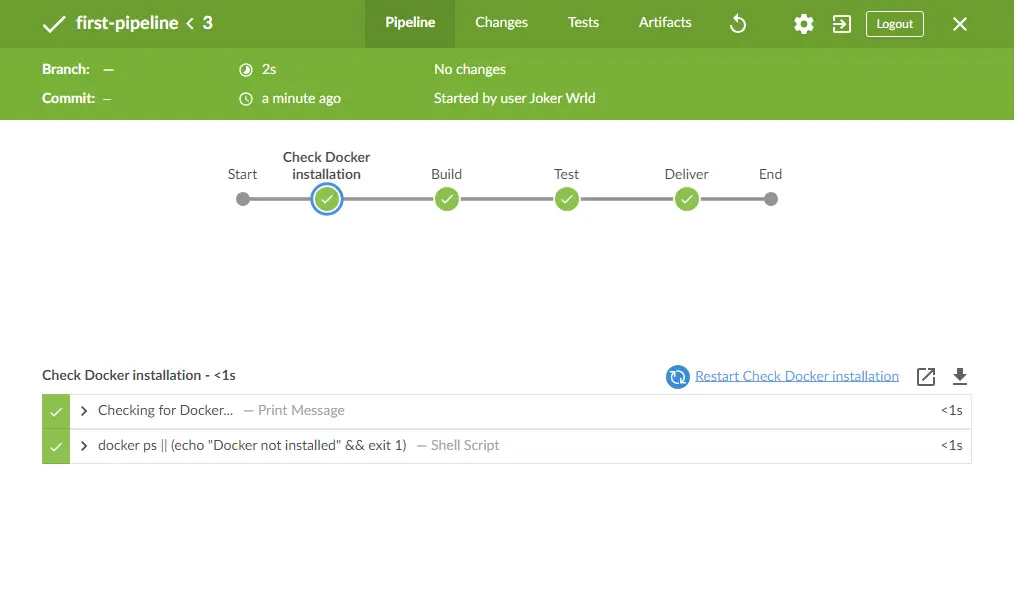
Let’s configure our first Jenkins pipeline by inserting the contents of our Jenkinsfile into the script area of the Pipeline job type.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Check Docker installation') {
steps {
echo 'Checking for Docker...'
sh '''
docker ps
'''
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo 'Building...'
sh '''
echo "Doing build stuff..."
'''
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
echo 'Testing...'
sh '''
echo "Doing test stuff..."
'''
}
}
stage('Deliver') {
steps {
echo 'Deliver...'
sh '''
echo "Doing delivery stuff..."
'''
}
}
}
}
After running the pipeline we can view our results in Blue Ocean interface: