Proxmox Essentials: Building a Robust Virtualization Environment
Proxmox Virtual Environment (Proxmox VE) is an open-source platform that combines two virtualization technologies: KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) for virtual machines and LXC (Linux Containers) for lightweight container-based virtualization. This powerful solution allows users to manage virtual machines, containers, storage, and networking through a web-based interface.
Installation
Check the Get Started Guide on How To Install Proxmox VE
During the installation, you can configure network settings. If you prefer to use DHCP initially, leave the settings as is. For those who want to set a static IP later, proceed with DHCP for now.
Setting Static IP Post-Installation:
You can also separate bridge networking to use custom IP rage for your VMs and LXCs see post.
After completing the Proxmox installation, you can set a static IP by modifying the network configuration file or in DHCP setting of your router. Connect to the Proxmox host using SSH or directly through the console, and edit the network configuration file:
1
nano /etc/network/interfaces
Locate the line containing
iface vmbr0(or your relevant interface) and change it to:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
auto lo iface lo inet loopback iface eno1 inet manual auto vmbr0 iface vmbr0 inet static address 192.168.1.10/24 gateway 192.168.1.254 bridge-ports eno1 bridge-stp off bridge-fd 0 iface enx98e74303cde3 inet manual iface wlp0s20f3 inet manualSave the file and restart the networking service:
1
service networking restart
First Setup
Disable Commercial Repositories
Add No-Subscription repository:
1
echo 'deb http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pve bookworm pve-no-subscription' > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-no-subscription.list
Disable the enterprise repo:
1
sed -i 's/^deb/#deb/g' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-enterprise.list
Disable the ceph repo:
1
sed -i 's/^deb/#deb/g' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ceph.list
To install the newest updates run:
1
apt update && apt dist-upgrade -y
1
reboot
Remove Subscription Alert
1
sed -i.backup -z "s/res === null || res === undefined || \!res || res\n\t\t\t.data.status.toLowerCase() \!== 'active'/false/g" /usr/share/javascript/proxmox-widget-toolkit/proxmoxlib.js && systemctl restart pveproxy.service
Cloud-Init Image Template
Choose your Ubuntu Cloud Image
Download Ubuntu (replace with the url of the one you chose from above)
1
wget https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/jammy/current/jammy-server-cloudimg-amd64.img
Create a new virtual machine
1
qm create 8000 --memory 4096 --core 4 --name ubuntu-cloud --net0 virtio,bridge=vmbr0
Import the downloaded Ubuntu disk to local-lvm storage
1
qm importdisk 8000 jammy-server-cloudimg-amd64.img local-lvm
Attach the new disk to the vm as a scsi drive on the scsi controller
1
qm set 8000 --scsihw virtio-scsi-pci --scsi0 local-lvm:vm-8000-disk-0
Add cloud init drive
1
qm set 8000 --ide2 local-lvm:cloudinit
Make the cloud init drive bootable and restrict BIOS to boot from disk only
1
qm set 8000 --boot c --bootdisk scsi0
Add serial console
1
qm set 8000 --serial0 socket --vga serial0
DO NOT START YOUR VM
Now, configure hardware and cloud init, then create a template and clone. If you want to expand your hard drive you can on this base image before creating a template or after you clone a new machine. I prefer to expand the hard drive after I clone a new machine based on need.
Create template
1
qm template 8000
Clone template
1
qm clone 8000 101 --name homelab --full
To use cloud-init, click on the new VM you made, go to
Cloud-Inittab and customize your settings and click onRegenerate Imageand that’s it! Start your new cloned VM and after waiting for the boot sequence to finish you should get directly to a login prompt. Enjoy!
Resize Proxmox VM
1 2 3
qm shutdown 101 qm set 101 --memory 8192 --core 4 qm resize 101 scsi0 +80G
Attach Pass Through Disk
Identify Disk
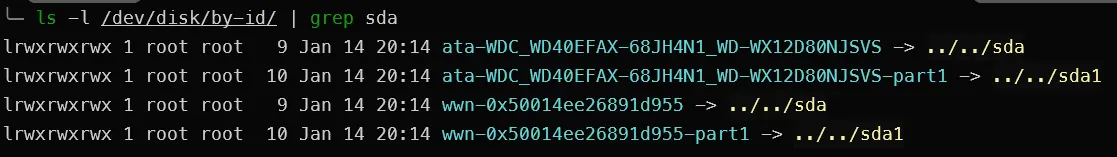
When attaching pass-through disks in Proxmox, it’s crucial to use stable device paths like /dev/disk/by-id/ instead of generic names like /dev/sdc, as the latter can change between reboots. Follow these steps to identify the disk:
1
ls -l /dev/disk/by-id/ | grep sda
The output should resemble something similar to the following, where you match the serial number with the physical disk:
Update Configuration
Hot-Plug/Add physical device as new virtual SCSI disk
1
qm set 115 -scsi1 /dev/disk/by-id/ata-WDC_WD40EFAX-68JH4N1_WD-WX12D80NJSVS
Hot-Unplug/Remove virtual disk
1
qm unlink 115 --idlist scsi1
Add Additional Hard Drive to Proxmox
To add an additional hard drive to your Proxmox server, follow these steps:
Connect the Hard Drive:
Physically connect the hard drive to your server.
Log in to the Proxmox console or connect via SSH from another computer.
Identify the New Disk:
Use the following command to identify the new disk:
1
lsblk
Look for the disk names like
sdaandsdb. Work with the drive that has a higher size.
Format the Drive:
Ensure you have the
partedtool installed. If not, install it using:1 2
apt policy parted apt install partedCreate a new partition table of type GPT:
1
parted /dev/sda mklabel gpt
Confirm the action when prompted.
Create a new primary partition with Ext4 filesystem using 100% of the disk:
1
parted -a opt /dev/sda mkpart primary ext4 0% 100%Check the new layout with:
1
lsblk
Create Ext4 Filesystem:
Create an Ext4 filesystem on the newly created partition (sda1 in this case):
1
mkfs.ext4 -L hdd_storage /dev/sda1
Mount the New Disk:
Create a new directory to mount the partition:
1
mkdir -p /mnt/hdd_storage
Modify
/etc/fstabto automatically mount the partition upon system boots:1
nano /etc/fstab
Add the following line:
1
LABEL=hdd_storage /mnt/hdd_storage ext4 defaults 0 2
Mount the drive:
1
mount -aConfirm the mount by checking with:
1
lsblk
The /dev/sda1 should be mounted as /mnt/hdd_storage.